Global trade never rests and neither does trade compliance.
The year 2024 was marked by a whirlwind of regulatory updates, high-stakes enforcement actions, and evolving export compliance requirements that kept businesses on their toes. From record-breaking penalties to shifts in enforcement priorities, the updates from regulatory agencies often read like the year’s biggest headlines—dramatic, impactful, and impossible to ignore.
Key enforcement agencies in the United States, including the Department of Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) and Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), the Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS), the Department of State (DOS), the Department of Justice (DOJ), and the Department of Homeland Security/Customs and Border Protection (DHS/CBP), played pivotal roles in shaping trade compliance this year. Their efforts ranged from sanctioning violators to cracking down on export control breaches and addressing supply chain security issues.
Beyond the U.S., the global trade compliance landscape saw significant activity from the European Union (EU) via the European Commission (EC), the United Nations (UN), and the United Kingdom (UK). These jurisdictions reinforced their commitment to international trade rules, with the EU focusing on export controls and sanctions, the UN emphasizing global standards through UN Security Council (Sanctions Committee), and the UK strengthening its independent post-Brexit enforcement mechanisms within the Export Control Joint Unit (ECJU), the Office of Financial Sanctions Implementation (OFSI), and His Majesty’s Revenue and Customs (HRMC), amongst others.
Complying with each agency in every jurisdiction relevant to your business and partners is increasingly complex. As we prepare for what comes in 2025, we look back on the year, exploring the key trends and the five major themes that shaped global trade compliance in 2024.
Key Takeaways
- 2024 was a year of record-breaking fines and penalties for violating trade compliance regulations.
- A series of new rules from key agencies have dictated an evolving reality of trade and export compliance regulations.
- A multiagency supply chain compliance crackdown is well underway with a focus on forced labor and sanction evasion.
- Sanction designations increased globally across jurisdictions, but they aren’t always comparable, necessitating a mature sanctions screening program.
- Trade compliance technology plays a mission-critical role in protecting business operations and advancing export compliance programs is necessary to avoid significant fines.
1. The Year of Record-Breaking Penalties
A few notable enforcement actions and cases that showcase expanding and increasing penalties related to export controls and trade and financial sanctions:
- FinCEN’s Landmark Fine: A record $1.3 billion penalty was imposed on a major U.S. bank for lapses in transaction monitoring and customer due diligence, which enabled illicit trade activities and violated the Bank Secrecy Act and anti-money laundering regulations. This unprecedented fine highlights the severe consequences of failing to implement robust regulatory compliance programs.
- OFAC’s long arm delivers heavy penalties: The “honor” of the largest fine of the year issued by OFAC goes to a Thailand-based enterprise, which was fined $20,000,000 to settle its alleged civil liability for 467 apparent OFAC sanctions violations involving Iran. This serves as a reminder that both U.S. and non-U.S. organizations need to have the right OFAC compliance systems in place.
- European sanctions enforcement hit new milestones: European enforcement of sanctions more than doubled in 2024, as agencies across the UK, the EU, and individual member states intensified efforts to ensure compliance. The largest fine of the year in Europe was imposed by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) on a prominent UK bank, which faced a £29 million penalty for deficiencies in its sanctions screening systems and internal controls.
- BIS clampdown on unauthorized technology exports: Several companies faced significant fines for exporting controlled technology to restricted countries, reinforcing BIS’ commitment to safeguarding critical technologies through the expanded Disruptive Technology Strike Force. Notably, an electrical and electronics manufacturer was fined $5.8 million for shipping items to restricted parties linked to China’s military electronics programs. Look at the BIS eBook “Don’t Let This Happen to You” to learn more.
- DOS amplifies efforts to ensure ITAR compliance: The DOS remains vigilant in addressing violations of the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR). This is illustrated by high-profile settlements, such as the $200 million agreement with a major defense contractor. The enforcement action was made possible by improperly managed successor liability risks.
- DOJ’s increased FCPA and national security focus: The DOJ intensified its efforts to prosecute entities for violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) as well as for circumventing export controls and sanctions. In 2024, the DOJ reported 23 FCPA-related enforcement actions, marking an increase compared to 2023. This included one of the year’s largest fines, exceeding $360 million, imposed on a defense contractor for FCPA and ITAR violations. Additionally, the DOJ recorded a 28% rise in prosecutions of individuals involved in sanctions evasion.
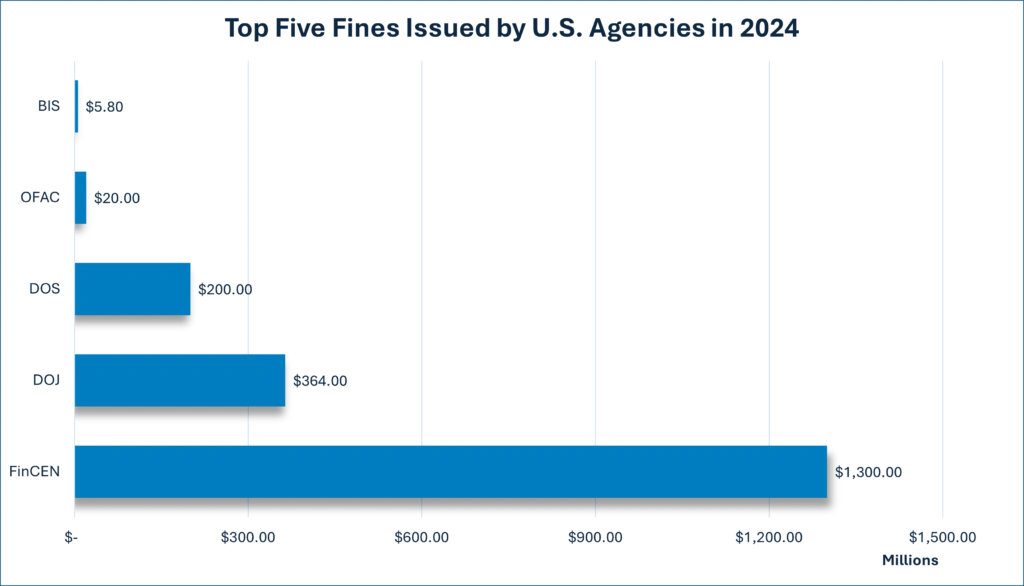
Figure1: The financial stake of non-compliance
Source: FinCEN, OFAC, DOS, DOJ, and BIS
| Agency | Fine Amount (Euro) | Case Description |
| FCA (UK) | £29 million (~€34.5M) | Sanctions violations by a major financial institution. |
| Customs (Lithuania) | €13.61 million | Fined for sanctions evasion by exporting vehicles to Russia through third countries Belarus, Kazakhstan and Turkey. |
| FCIS (Lithuania) | €8.24 million | Lithuania’s Financial Crimes Investigation Service (FCIS) fined a Crypto firm for breaching EU Russia sanctions. |
| Customs (Poland) | €2.78 million | Breach of asset freezes and circumvention of Russia sanctions. |
| Customs (Germany) | €2.50 million | Unauthorized exports of luxury cars to Russia in violation of existing EU sanctions. |
Table 1: European Sanctions Enforcement: Highest Individual Fines, Penalties, and Confiscations
These sky-high fines underscore the importance of export compliance solutions and how enforcement priorities have changed — and will continue to increase in the future. Additionally, these enforcement actions highlight the necessity of monitoring evolving global sanctions and implementing comprehensive internal compliance processes.

Want to see how Descartes’ award-winning trade compliance solutions can help your organization?
2. New Rules, New Realities
Regulatory bodies across the globe issued new regulations, mandates, and guidance throughout the year, making it a pivotal period for trade compliance professionals.
Key Events
Here are a few significant new rules that emerged, shaping the evolving reality of regulatory requirements:
- 10-year recordkeeping mandate: In September 2024, OFAC implemented a new 10-year recordkeeping mandate that doubled the previous duration of retaining applicable records. This change also extends the window of possible enforcement actions for violations, raising operational and IT compliance challenges for businesses.
- BIS export control updates: the agency rolled out a series of updates to export controls and policies to sharpen its focus on emerging technologies, accountability, and export diversion risks. Major changes include stricter reforms to voluntary self-disclosures (VSD), guidelines around the first-ever “address-only” listings on the Entity List, and introduction of the Trade Integrity Project list, adding another layer of scrutiny to export transactions.
- Revised guidance on international trade and partnerships: The UK government enacted the Trade, Aircraft, and Shipping Sanctions (Civil Enforcement) Regulations 2024, enhancing the Department for Business and Trade’s powers to enforce trade sanctions through the newly established Office of Trade Sanctions Implementation (OTSI).
- G7 advisory on Russia sanctions evasion: A unified stance from the G7 aimed at combating Russian sanctions evasion introduced tighter controls, compelling businesses to reassess compliance frameworks for supply chain integrity.
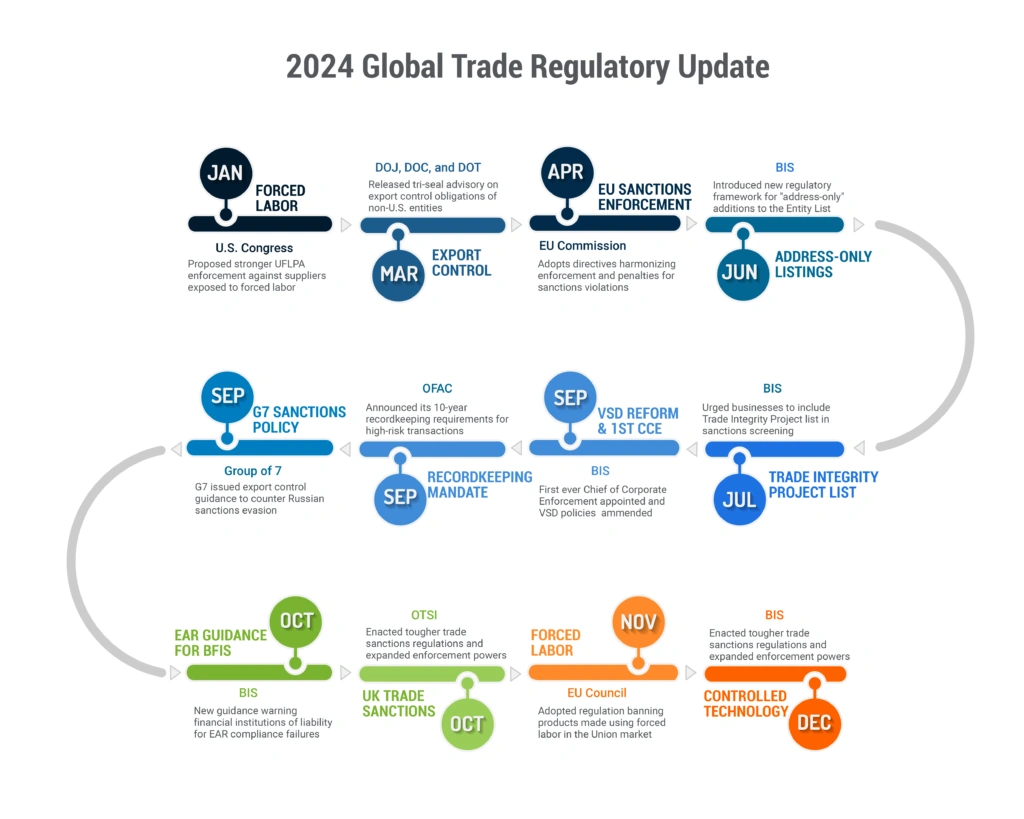
Figure 2: Timeline of Major Regulatory Transformation in 2024
3. The Supply Chain Compliance Crackdown
There was a global uptick in regulatory scrutiny of supply chains in 2024, largely related to forced labor practices, and broader environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals.
Key Events
This year shone a light on the rising emphasis on supply chain compliance and transparency, with governments worldwide stepping up enforcement efforts. Major events include:
- Increased forced labor enforcement: CBP intensified its efforts under the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA), detaining shipments suspected of links to forced labor. According to CBP enforcement statistics, $1.73 billion worth of shipments were denied last year— a new annual record for UFLPA-related enforcement actions.
- Global action on adverse human rights and environmental impact: Beyond the U.S., jurisdictions such as the EU, UK, and Canada introduced and enforced regulations targeting forced labor. Notably, the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) mandated enhanced supply chain transparency, impacting numerous multinational companies.
- Multi-agency coordination: Coordinated efforts by BIS, OFAC, and DOJ dismantled complex sanctions evasion networks that leveraged global supply chains to obscure illicit trade. A prominent example was BIS export control reforms targeting transnational networks tied to restricted technologies and goods flowing to sanctioned entities. A series of transformative new rules aimed at tightening supply chain controls related to military, intelligence, and security activities under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR).
The escalating frequency and severity of enforcement actions have greatly influenced global supply chain compliance strategies. Companies are increasingly prioritizing enhanced due diligence programs to address forced labor risks, ensure ESG alignment, and mitigate sanctions exposure. These actions showcase the implications of robust supply chain compliance solutions with denied party screening capabilities to vet trade partners and third-party relationships.
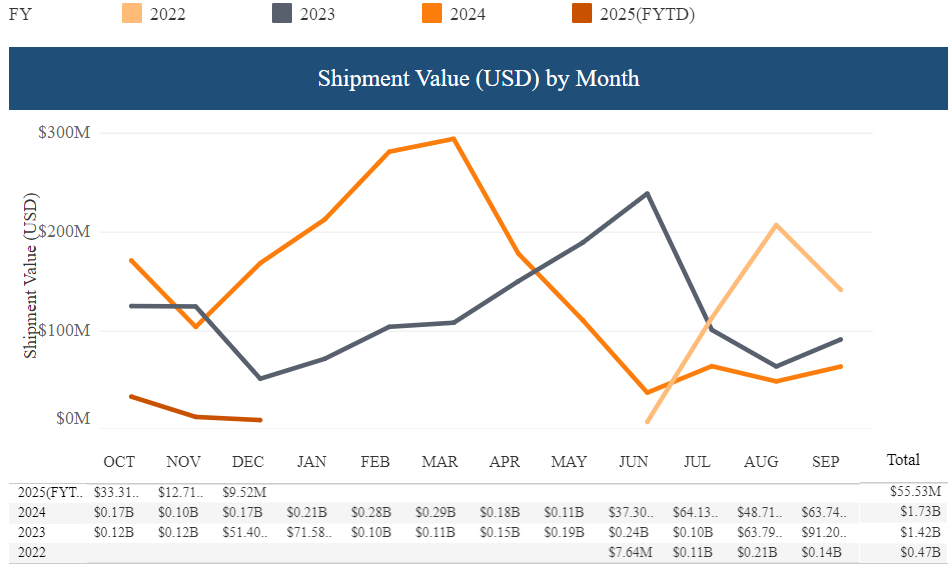
Figure 3: CBP stats on the value of shipments detained June 2022 – December 2024
Source: CBP
4. The Global Surge in Sanctions Designations
Governments around the world implemented more stringent sanctions, including a growth in the scale and pace of designations. This surge reflects the intensifying geopolitical and humanitarian challenges worldwide.
Key Events
A few key designations that organizations need to understand include the following:
- U.S. – A Year of Escalation: OFAC and BIS made significant additions to their respective Specially Designated Nationals (SDN) and Entity Lists. With over 300 additions to the Entity List, 2024 was one of the BIS’ busiest years, a trend we don’t expect to slow down. Similarly, DHS/CBP added 66 entities to the UFLPA Entity List—a 200% increase over the combined entity list additions of 2022 and 2023.
- EU – Strengthening Sanctions Enforcement: The European Union ramped up its restrictive measures with over 600 entity list additions primarily targeting Russian aggression in Ukraine.
- UK – Emerging Sanctions Powerhouse: Since leaving the European Union, the United Kingdom has become more prominent in shaping its own sanctions regime. With its independent sanctions framework, the UK introduced several impactful measures, reflecting its growing influence in the global sanctions arena.
- UN – Global Coordination on Humanitarian Concerns: The UN has made high-profile designations, including sanctions against entities involved in illicit mineral trade funding armed conflict in Africa. The UN Security Council adopted 46 resolutions in 2024.
The heightened operational complexity facing businesses also overlaps with sometimes inconsistent sanctions lists across varying jurisdictions. This sprawling network of regulations and designations requires robust denied party screening efforts and export license management, especially for multinational organizations.
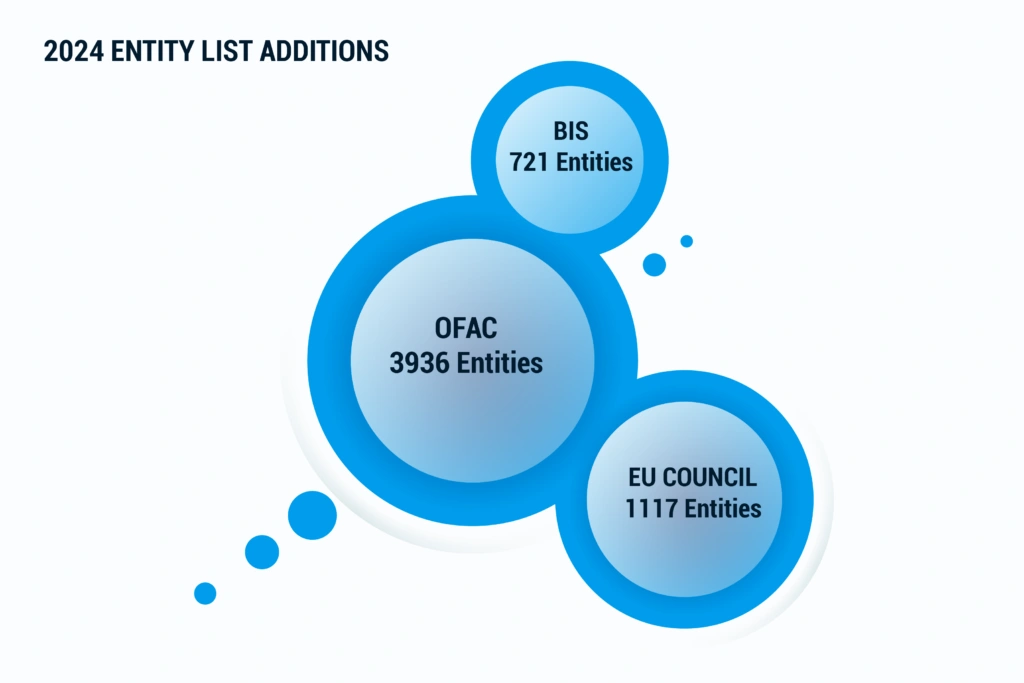
Figure 4: 2024 Entity List Additions by the European Council, OFAC, and BIS
Source: Descartes trade compliance content experts
5. Technology at the Forefront of Trade Compliance
Technology and trade compliance became ever more intertwined as businesses and regulators alike leaned heavily on digital tools to address the growing complexity of global trade. With increasing regulations and heightened risks, advanced export compliance solutions emerged as indispensable.
Key Events
Below are some significant advancements in the adoption of export and trade compliance software solutions in 2024:
- Increased Reliance on Technology in Enforcement: Regulatory bodies have significantly expanded their use of technology to monitor and enforce compliance, with advanced data analytics playing a central role in identifying violations or suspicious activities. Regulators are also increasingly considering a company’s adoption of compliance technologies when conducting audits and assessing penalties for violations. Example: BIS issued new guidance for financial institutions on export control compliance, emphasizing the use of technology to detect unlawful dual-use trade.
- Regulatory Scrutiny of Advanced and Emerging Technologies: Regulators have increased their focus on emerging technologies such as quantum computing and biotechnology. New export control measures have been implemented to prevent these technologies from being exploited for military or unauthorized purposes.
- Growing utility of AI and machine learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have transformed core trade compliance processes, including export classification, and export licensing. AI-driven tools streamline trade compliance, in particular managing denied party screening workload, minimizing false positives and boosting the operational efficiency of compliance teams.
- Emphasis on cybersecurity for platforms: 2024 witnessed cybersecurity breaches affecting trade compliance systems. In one high-profile instance, hackers threatened to leak sensitive data gained from these systems. It’s crucial for organizations to thoroughly vet their trade compliance software vendors to ensure they have effective cybersecurity measures in place.
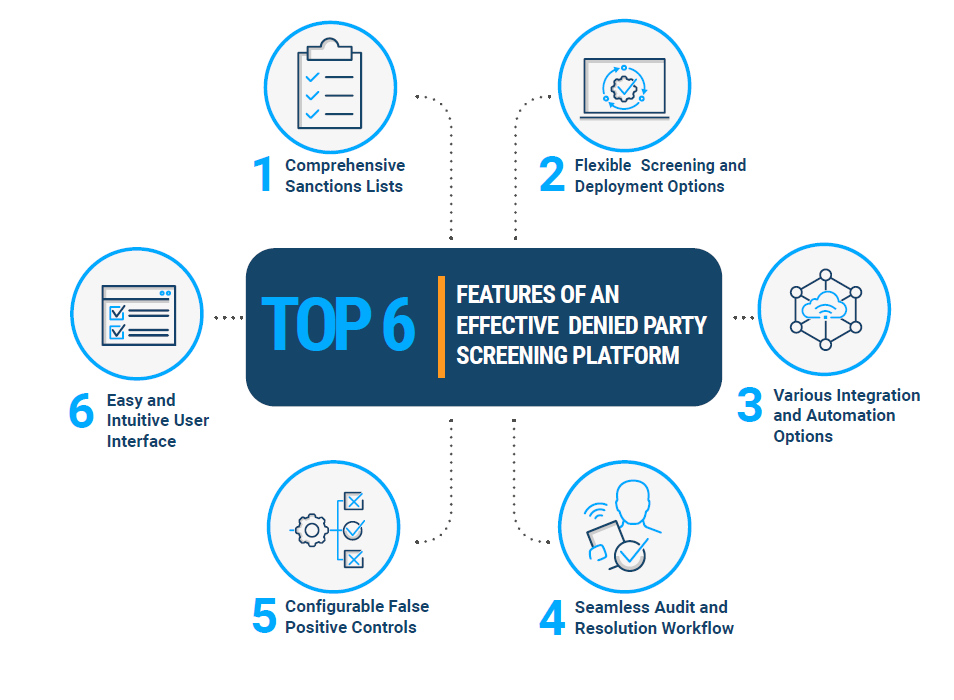
Figure 5: Features of an effective denied party screening software solution
Looking Ahead: 2025 Trade Compliance Priorities
What can we learn from 2024 to prepare for 2025 and the overall future of trade compliance? At the start of the previous year, we made several predictions of what trade compliance in 2024 will be shaped by, see how well we did. How might the themes we’ve explored today inform the future of trade compliance? Let’s break down how we see the future of trade compliance evolving in the coming years:
- Emerging enforcement trends: We expect to see more regulations focusing on securing and safeguarding the Information and Communications Technology and Services (ICTS), stricter controls on AI exports, and semiconductor regulations. Businesses operating in these spaces should brace for heightened trade compliance demands and prioritize supply chain transparency in their operations.
- Potential shifts in agency priorities: 2024 saw elections worldwide that will likely bring changes in priorities and policies. For example, the US is leading the charge in trade sanctions enforcement, the second Trump presidency could bring significant turbulence in U.S. trade policy. Historically, Trump’s administration emphasized unilateral trade measures, which may result in shifts in agency enforcement priorities, including increased sanctions and tariff actions. Businesses should anticipate more aggressive regulatory changes and prepare to pivot quickly.
- Supply Chain Compliance and Resilience: Supply chain compliance is expected to take center stage in 2025. Key drivers include intensified scrutiny of forced labor practices, ESG expectations, and the growing use of tariffs to achieve trade objectives. Companies should integrate supply chain resilience into their trade compliance programs, ensuring they can navigate both regulatory demands and operational disruptions.
- Global Influences on Compliance: Geopolitical tensions will continue to shape trade compliance strategies. Ongoing conflicts, such as the war in Ukraine and unrest in Syria, will likely lead to additional sanctions and restrictive measures.
- Technology continues to play a critical role: As compliance demands increase, so does the reliance on advanced technology to meet these requirements. In 2025, artificial intelligence and machine learning will play an even larger role in enabling efficient denied party screening, export classification, and supply chain visibility.
The future is uncertain but implementing effective policies and platforms that protect your compliance standing is of the utmost importance. For a deeper dive into what to expect, read our article on the top 5 trade compliance trends to look out for in 2025.
Actionable Takeaways for Success
- Adopting advanced trade compliance systems: Evaluating existing systems to ensure alignment with regulatory trends and trade compliance obligations is essential for maintaining efficiency and reducing risk. Where necessary, invest in advanced tools and technologies to streamline key export and trade compliance processes. Enhanced capabilities, such as automation and data analytics, can help mitigate vulnerabilities, improve accuracy, and ensure readiness to adapt to evolving global trade requirements.
- Fostering employee awareness: Establishing ongoing training programs on evolving regulations and trade compliance best practices is critical to empowering employees to uphold standards and mitigate risks. By fostering a culture of compliance through regular education, practical workshops, and real-world scenario training, you can ensure your team remains informed and prepared to navigate the complexities of global trade regulations.
- Conducting routine audits: Regular assessments of trade compliance systems and practices are essential for identifying vulnerabilities and addressing potential risks. These assessments ensure that processes uncover gaps or inefficiencies and provide opportunities for continuous improvement. By integrating routine audits into your compliance strategy, you can enhance operational accuracy and reduce the likelihood of violations.
- Strengthening supply chain compliance measures: To ensure resilience amid geopolitical tensions, evolving trade policies, and cybersecurity threats, emphasize diversified sourcing and risk management. Advanced trade compliance tools and proactive strategies will be critical to meeting these demands and safeguarding competitive advantage.
- Partnering with experts: Collaborating with trusted trade compliance solution providers is a strategic way to simplify navigating complex and evolving regulatory environments. These experts offer specialized knowledge, tools, and resources to help organizations stay ahead of global trade requirements.
Transform Trade Compliance Complexity into Clarity with Descartes Solutions
2024 demonstrated the dynamic nature of trade compliance, marked by intensified enforcement actions, evolving regulations, and increased global scrutiny on issues like advanced technologies, supply chain compliance, and forced labor practices.
With Descartes’ robust trade compliance solutions and industry expertise, businesses can confidently navigate this ever-changing landscape. Our advanced capabilities streamline complex denied party and OFAC screening processes, enhance supply chain visibility, automate export licensing, and ensure seamless adherence to regulatory requirements, empowering organizations to implement the actionable strategies outlined for 2025.
Request a demo to see how our award-winning technology can help you stay ahead of export compliance challenges and simplify trade complexity.
Find out what our customers are saying about Descartes Denied Party Screening on G2 – an online third-party business software review platform. Additionally, you can read this essential buyer’s guide to denied party screening to help you select a solution that fits your needs.