Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are powerful tools for companies looking to expand their market presence, diversify their portfolios, or gain access to new technologies. However, while these strategic moves can propel growth, they also come with substantial risks, particularly in the realm of export compliance. Failing to perform thorough due diligence on the target company’s export practices can lead to significant legal, financial, and operational repercussions.
Consider a recent example of serious International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) compliance violations uncovered during a major M&A. The U.S. Department of State recently settled with an aerospace and defense technology company in a case involving multiple violations, resulting in hundreds of millions of dollars in fines. The case involved the unauthorized exchange of defense articles, and the sharing of technical data controlled under ITAR. After the company’s voluntary disclosure and cooperation with the Department’s review, the federal government settled on a hefty fine and a three-year consent agreement to remediate the violator’s compliance program. The U.S. Department of State’s press release indicates that the violations occurred between August 2017 and September 2023. This timeline suggests that the violations took place prior to the acquisition in April 2020 and continued thereafter.
This case illustrates the serious compliance risks associated with M&A transactions and the severe consequences companies face if export compliance is overlooked during the due diligence phase. Entities considering an M&A must take a proactive and thorough approach to the due diligence process to secure their operations from these risks.
Key Takeaways
- Hidden Liabilities: M&A can expose companies to hidden liabilities, including violations of trade sanctions and export control regulations like ITAR.
- Successor Liability: Acquiring companies can be held liable for past export control violations committed by the target company.
- Thorough Due Diligence: A comprehensive export compliance due diligence process is crucial to mitigate risks and ensure successful M&A integration.
- Technology & Automation: Technology solutions can streamline export compliance due diligence, saving time and resources.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Maintaining a robust export compliance program is essential after the M&A.
Understanding Successor Liability in Mergers & Acquisitions
A critical aspect of export compliance risk in M&A is the concept of successor liability. This legal principle holds that a company acquiring another entity may inherit the legal liabilities of the acquired business, including any past export control violations. The doctrine applies even if the acquiring company was unaware of the misconduct at the time of the transaction. This means that regulators expect organizations to proactively manage and understand their export compliance obligations. As such, acquiring firms can still be held accountable for fines, penalties, and operational limitations, if they don’t identify and address any compliance risks inherited from the transaction.
The successor in an M&A deal should not simply sweep uncovered violations under the rug or expect elapsed time to render them inconsequential. A violation uncovered at any time should promptly be reported to the appropriate authorities. If a violation comes to light before the deal closes, the responsible company should self-disclose. However, if they refuse, the other party to the M&A should report the violation and consider whether or not to proceed with the transaction.
Impact of Successor Liability on a Business
The implications of successor liability can be far-reaching, particularly in the context of export controls. This can be seen in a number of enforcement actions and penalties imposed on organizations for previous violations of export control laws by the acquired entity:
- Inherited Export/Sanctions Violations: A chemical and biotechnology company faced export compliance issues after acquiring a subsidiary with prior Export Administration Regulations (EAR) violations. The subsidiary had exported controlled substances without the necessary export licenses. Notably, although the biotechnology company had only acquired partnership interests, it was held legally responsible under successor liability, as the acquired firm was now defunct. This case underscores how regulators apply successor liability rules to enforce export controls aggressively even when the defaulting entity no longer exists.
- Financial Penalties: The financial impact can be significant. On March 30, 2023, an American multinational financial services company agreed to pay $30 million to settle penalties with OFAC for violating sanctions on Iran, Syria, and Sudan. These violations stemmed from its acquisition of another U.S. financial institution, which had legacy software providing financial services in sanctioned regions via a European bank. OFAC found that the acquiring company lacked oversight, allowing the violations to continue for seven years post-acquisition. This aggravating factor led to the high monetary fine. The key takeaway from this case is the need for rigorous internal trade controls when integrating acquired services and systems.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: In March 2019, an American tool company reached a settlement with the U.S. Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) and agreed to pay $1,869,144 in penalties for violations of the Iranian Transactions and Sanctions Regulations. The violations were committed by a recently acquired Chinese subsidiary, which was found to be involved in activities defying U.S. trade sanctions against Iran. During the acquisition, the U.S. tool manufacturer initially identified that the Chinese company had exported products to Iran. As a condition of the sale, the target company was required to stop these transactions. However, post-acquisition, the U.S. tool manufacturer did not maintain ongoing monitoring to ensure compliance with this requirement. This case demonstrates the risks of successor liability when export compliance oversight is not consistently enforced and also highlights OFAC’s continued focus on holding companies under U.S. jurisdiction accountable for the actions of their foreign subsidiaries.
- Operational Restrictions: In cases where the target company has violated export controls or trade sanctions, the successor company may face operational restrictions. These can include prohibitions on certain types of exports or imports, leading to a loss of market access and revenue. Consider, for example, the OFAC settlement with a business analytics firm for apparent violations of Ukraine-related sanctions regulations. These violations stemmed from actions by an acquired research firm, which had reissued and redated invoices to an OFAC-listed entity. The sensitive nature of the business analytics firm’s industry compounded the impact of these compliance issues, ultimately affecting the firm’s operations. This case highlights the importance of rigorously examining acquired entities’ practices to avoid unexpected liabilities that can impede business continuity.
- Reputational Damage: Non-compliance can tarnish a company’s reputation, damaging relationships with stakeholders. On June 13, 2019, the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) announced a settlement with online travel services company, failing to inform a new subsidiary about U.S. compliance requirements led to violations, severely affecting their brand image.
Export control violations are very serious and can result in criminal prosecution, depending on the nature of a violation. Export compliance violations are often seen as a threat to national security and inflict correspondingly legal repercussions.
How can businesses mitigate the risk of successor liability and other export compliance risks when considering an M&A deal?
Identifying and Addressing Export Compliance Liabilities in M&A
When engaging in M&A, many organizations focus on financial and operational synergies but often overlook export compliance risks. These hidden liabilities can create significant challenges if not properly addressed:
- Regulatory compliance misalignment – M&A transactions, especially involving foreign parties or controlled goods, may have differing export control standards which can expose companies to a wide range of regulatory risks. All parties must have robust compliance programs with ongoing audits and training to close any gaps and adhere to applicable regulations.
- Acquired sanctions violations – post-merger, a company may discover that the acquired party had undisclosed export control violations or even made transactions with sanctioned or denied parties and is thus obligated to disclose and take responsibility for such infractions.
- Due diligence failures – Parties to an M&A may rush the deal without investigating current compliance practices and planning for ongoing compliance which also includes employee conduct. This can lead to costly violations that diminish the deal’s profitability.
- Third-party risks – Companies may face difficulties when they inherit the risk of engaging in trade with sanctioned entities. Suppliers, vendors, customers, and other third-party relationships that were transferred as part of the M&A may involve restricted or sanctioned parties with ongoing commitments.
- Reputational risks – Solidifying an M&A deal with a company that is later found to have violated international trade laws will negatively affect the reputation of the emerging entity.
Avoiding these risks and making a successful M&A in compliance with export regulations is possible, especially with the help of trade compliance tools.
Best Practices for Managing Export Compliance Risks in M&A
Before acquiring or merging with another company, an organization must thoroughly examine the business practices and export compliance program of the company in question. Companies must prioritize this aspect to avoid inheriting liabilities that could jeopardize their financial stability and reputation.
Figure 1: Export Compliance Best Practices for Reducing M&A Successor Liability
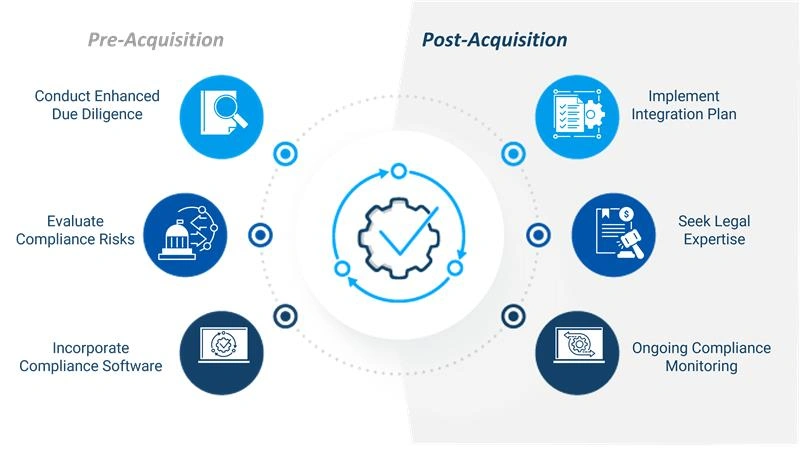
The following best practices will help to safeguard the organization against successor liability and maintain regulatory alignment.
- Conduct Enhanced Due Diligence: Assess the target company’s export compliance program and practices. This process involves examining their records and uncovering any historical compliance violations.
- Evaluate Compliance Risks: Even domestic mergers need careful review of export controls. If a newly acquired company employed foreign nationals without proper licensing, the buyer inherits responsibility for compliance actions, including licensing, disclosures, and penalties.
- Develop a Comprehensive Integration Plan: Develop a plan to adapt the compliance program for the merged entity, including training for all staff on current export regulations. Post-acquisition, a clear integration plan helps to align compliance programs between the entities.
- Engage Legal and Compliance Experts: Partner with M&A and export compliance specialists to navigate complex trade laws effectively.
- Implement Ongoing Export Compliance Monitoring: Put in place continuous compliance checks before, during, and after integration to address evolving risks.
- Incorporate Export Compliance Software: Use automation tools to streamline compliance due diligence, reduce human error, and boost confidence in adherence to export regulations.
Streamlining M&A Due Diligence with Export Compliance Software
The use of technology can enable companies to significantly enhance the effectiveness of their export compliance due diligence efforts and reduce the risk of violations. Here are key areas that can be streamlined with advanced export compliance solutions:
- Robust denied party screening – Incorporating denied party screening solutions early on significantly reduces M&A liabilities by automating the detection of high-risk entities. Capabilities like batch screening quickly vets all acquired parties against updated government and non-government watchlists, efficiently identifying denied or sanctioned entities. Furthermore, dynamic rescreening features automatically check for newly restricted entities. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of potential penalties due to missed screenings during the acquisition process.
- Automated export classification – Simplify the product classification process and avoid the legal and financial fallout of improper classification and minimizing the risk of non-compliance. In an M&A, automated export classification software ensures that all acquired products are correctly classified according to export control regulations. This reduces the risk of inheriting non-compliance liabilities from improper classifications and minimizes exposure to post-acquisition regulatory issues.
- Real-time export license management and tracking – Utilize technology to enable real-time tracking of export licenses, ensuring they are valid, updated, and that the terms of the licenses are being met. By tracking and managing licenses in real time, organizations can avoid liability for unauthorized trade activities, especially with ITAR or EAR-controlled items.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Gain critical insights into customers, vendors, and partners to strengthen due diligence and minimize M&A liability. Identifying risks such as forced labor, adverse media, corruption, and sanctioned ownership ensures a comprehensive understanding of potential compliance vulnerabilities. This supports regulatory alignment and promotes a more informed, risk-conscious integration process in mergers and acquisitions.
- Centralized export documentation management –Centralizing export records simplifies audit preparation and improves document accuracy, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing transparency for external scrutiny. For M&A due diligence, this makes it easier for the acquirer to review the company’s historical compliance records and export documentation.
- End-to-end workflow integration – Prioritize export compliance as a core component of both pre- and post-M&A company culture. By seamlessly integrating export compliance processes into existing workflows and creating a unified, streamlined process, companies can enhance accuracy and efficiency in their operations.
- Compliance training and resources – Continuous training across departments ensures company-wide awareness of trade laws, establishing a proactive compliance culture and reducing the chance of violations. Prioritize solutions and vendors who provide in-depth export compliance resources and free training.
How Descartes Solutions Can Help with Export Compliance During Mergers and Acquisitions
In mergers and acquisitions, thorough export compliance due diligence is essential to prevent inheriting liabilities that could harm a company’s finances and reputation. Several examples of enforcement actions highlight the risks of overlooking this step. Leveraging export compliance software can help identify potential compliance issues, allowing companies to assess whether to proceed with a deal or adjust terms to address any concerns.
Descartes offers a sophisticated suite of trade and export compliance tools that simplify the M&A due diligence process. These solutions streamline compliance management, enabling companies to conduct thorough due diligence efficiently, even in complex M&A transactions.
Beyond the acquisition phase, Descartes’ tools support long-term export compliance success, equipping restructuring organizations with resources for sustained regulatory adherence and risk management. Our comprehensive solutions provide end-to-end support with dedicated tools for integrated denied party screening, export license management, and documentation automation on one centralized platform. Contact us if you would like to learn more about our technology or request a demo to see it in action.